Aside from physical changes, pregnancy, childbirth, and parenthood are characterized by happy moments and challenging times. Every woman’s postpartum experience is different, influenced by various elements such as her body’s reaction, the delivery’s course, and the postpartum care. It is only natural for most women to consider the changes their bodies have experienced after giving birth. Vaginal laxity is an issue that frequently comes up during this postpartum phase. This article examines the various aspects of vaginal tightness after giving birth, highlighting the subtleties and nuances that affect this aspect of a woman’s postpartum recovery. Let’s talk about how to tighten your vagina after birth.
Vaginal Laxity: What Is It?
The condition known as vaginal laxity, or “looseness,” occurs when the vagina loses some of its firmness or tightness. The two most frequent causes of this are getting older and having children. This may result in decreased sexual satisfaction for the lady and her partner as well as low self-esteem for the woman. Thankfully, there are a number of therapies and exercises that help control and enhance this disease.
How to Handle Vaginal Tightness Following Delivery
For vaginal tightening following childbirth, a variety of techniques and interventions—from surgical to non-surgical procedures—have been investigated. It is imperative to acknowledge that the efficacy and suitability of these techniques exhibit variability and, in certain instances, involve possible hazards.
The following techniques have been thought of:
Procedure of Choice: Vaginoplasty
This is a surgical technique intended to treat vaginal laxity, or looseness, a condition that is frequently linked to events like childbirth. The goal of a vaginoplasty is to restore firmness and tone to the vaginal canal by tightening the muscles and tissues in the vagina. Here are some broad instructions on how to go about doing it:
Anaesthesia Administration:
To guarantee the patient’s comfort and pain management during the surgery, anesthesia is administered before the procedure begins.
Incisions in the Vaginal Canal:
The surgeon performs precisely timed incisions in the vaginal canal while under the effect of anesthesia. These cuts offer access to the sections that need to be adjusted.
Removal of Extra/Redundant Vaginal Mucosal Lining:
During the operation, extra or redundant vaginal mucosal lining—which is frequently linked to age and childbirth—is carefully removed.
Tightening of Underlying Muscles:
After that, any laxity in the underlying muscles of the vaginal canal is sutured back together. This step is essential to get the desired tightening effect.
Procedure for Suturing:
The surgeon carefully stitches the underlying muscles together to improve the stiffness and tone of the vaginal canal strategically.
Closure of Incision:
Dissolvable stitches are used to close the incisions carefully once the surgeon has achieved the desired result. An essential part of the surgical procedure is this closure.
Evaluation of the Outcome:
The surgeon evaluates the findings to make sure that the patient’s objectives and expectations are met and that the restoration of tone and firmness in the vaginal canal is safe.
Postoperative Care:
The patient is advised on how to take care of themselves after the treatment, and their healing process is closely watched to guarantee a speedy recovery.
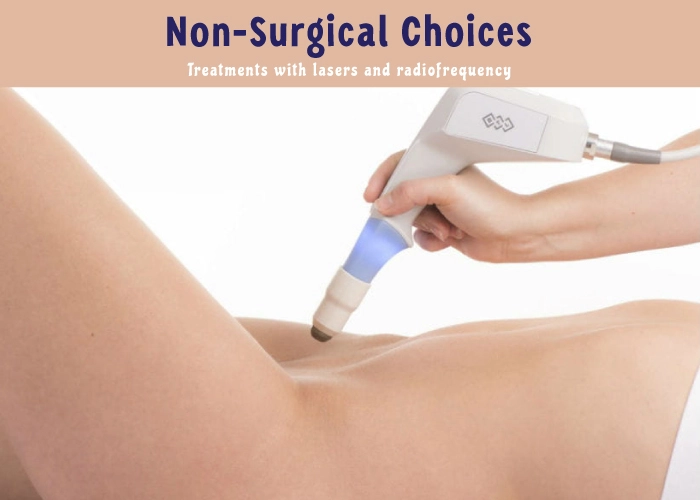
Non-Surgical Choices
Treatments with lasers and radiofrequency
These non-invasive, non-surgical methods of vaginal tightening aim and stimulate the vaginal tissues using radiofrequency (RF) or laser energy. The RF or laser energy emitted by the vaginally inserted probe promotes tissue regeneration, increased blood flow, and the formation of collagen. By doing this, it improves the vagina’s suppleness and tightness following childbirth. It can take multiple sessions to get the best results.
Kegel exercises
One of the most popular non-surgical methods for tightening the vagina after childbirth is this one. The pelvic floor muscles are rhythmically contracted and relaxed during Kegel exercises. There are no known negative effects to this economical, non-invasive technique. It is convenient to do in a standing, sitting, or lying down position, providing the user with versatility. Crucially, Kegel exercises don’t require any extra equipment.
Concealed Cones
Vaginal cones, sometimes referred to as vaginal weights, are a type of pelvic floor muscle resistance exercise. They are intended to support improved vaginal tightness following childbirth by toning and strengthening the muscles.
Electrical Stimulation of the Muscles
Electrical currents are used in a technique called neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) to induce muscle contractions. It can be used to strengthen and tone the pelvic floor muscles, which may assist to ease vaginal tightness following childbirth.
Gels for Vaginal Tightening
These gels are topical lotions that have been used to increase the firmness and flexibility of the tissue in the vagina. Although their precise mode of action is uncertain, they typically contain both natural and synthetic ingredients, such as hazel, allium, aloe vera, and other plant extracts. Usually, the tightening effect they provide lasts for a few hours before diminishing.
Advantages of Vaginal Tightening Following Delivery
- During sexual activity, it enhances friction and sensation.
- Enhances the pelvic floor muscles and relieves postpartum vaginal stiffness, which contributes to a more pleasurable and satisfying sexual experience for both partners.
- Focuses on issues related to vaginal laxity after childbirth and promotes positive body image, self-esteem, and general well-being.
- Aids in the treatment of various pelvic floor conditions, including stress, urine incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.
After giving delivery, how long does it take for the vagina to heal?
Every person has a unique pregnancy and delivery experience, and similarly, every person recovers differently after giving birth. The good news is that your vagina is elastic, meaning it will quickly revert to its original shape after accommodating your baby. The muscles can stretch and contract, even though the vagina may momentarily become more relaxed. Most women feel fully recovered in about 6 to 8 weeks on average. It could, however, go much more slowly or take much longer. Your vaginal muscles are more prone to become less supple if you have had numerous children.
Seek Expert Guidance on Vaginal Tightening Following Delivery:
While there are a number of non-surgical and surgical options for treating vaginal tightening following childbirth, it’s important to approach these with reasonable expectations and seek the advice of medical professionals for specific recommendations. While surgical alternatives like vaginoplasty offer more permanent remedies, non-surgical methods, including Kegel exercises, vaginal cones, neuromuscular electrical stimulation, and topical gels, offer non-invasive approaches.
In summary
After giving birth, it’s normal for your body to change, but you may improve and even restore your vaginal tone with the correct care. You can regain comfort and confidence in numerous ways, including through medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and Kegel exercises. Keep in mind that each woman’s body is different, so exercise self-compassion while pursuing your objectives.